Have you ever wondered what impact coffee has on your health and body? If you’re like many, savoring that morning cup of coffee might be one of the best parts of your day. This cherished beverage, globally consumed by millions, has sparked countless debates about its effects on health. In this comprehensive article, we’ll break down the various ways coffee influences your health and body, making it easier for you to understand and decide whether to embrace or limit your coffee habits.
The Basics of Coffee
Coffee is more than just a beverage; it’s a complex mix of substances that interact with your body in various ways. Originating from the beans of the Coffea plant, this drink has a rich history and diverse method of preparation. But what’s in it, and how might these components affect you?
What’s in Coffee?
Coffee beans contain several physiologically active compounds. Here’s a quick breakdown:
| Compound | Description |
|---|---|
| Caffeine | A natural stimulant known for its ability to boost alertness and reduce fatigue. |
| Antioxidants | Substances that can prevent or slow damage to cells caused by free radicals. |
| Diterpenes | Compounds with potential anti-inflammatory effects but may raise cholesterol levels. |
| Chlorogenic Acid | A polyphenol that has been shown to affect glucose metabolism and weight management. |
Understanding these components is crucial as they each contribute to how coffee affects your body.
Coffee and Your Brain
Coffee’s impact on your cognitive functions is perhaps one of the reasons it’s so beloved. But how does it really work?
Boosts Alertness and Mental Clarity
Caffeine, the primary stimulant in coffee, blocks the inhibitory neurotransmitter adenosine. This increases neurotransmitter firing, leading to improved energy levels, mood, and various aspects of brain function.
Protects Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
Some studies suggest that long-term coffee consumption may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. The antioxidants in coffee can protect neurons from damage and bolster overall brain health.
Impact on Sleep
While coffee can enhance alertness, consuming it late in the day can disrupt sleep patterns. Caffeine has a half-life of about 5-6 hours, so it’s best to enjoy it earlier in the day if you’re sensitive to its effects.
Coffee and Your Heart
Your heart health is a critical aspect of overall wellness. Coffee’s effects on your cardiovascular system can be both beneficial and problematic, depending on various factors.
Short-Term Effects on Blood Pressure
Caffeine can cause a short-term spike in blood pressure. However, this effect diminishes with regular consumption as your body builds a tolerance.
Long-Term Heart Health
Moderate coffee consumption has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke. The antioxidants in coffee may help to protect the heart and blood vessels from damage.
Cholesterol Levels
Unfiltered coffee, such as French press or Turkish coffee, contains compounds called diterpenes that can increase LDL cholesterol levels. Opt for filtered coffee to minimize this effect.
Coffee and Digestive System
Your digestive system plays a vital role in overall health, and coffee can impact it in various ways.
Gut Health
Coffee has a stimulating effect on gastric acid secretion, which can aid in digestion but may also cause discomfort or exacerbate conditions like acid reflux or GERD in some individuals.
Impact on Liver Health
Several studies have indicated that coffee drinkers have a lower risk of developing liver conditions like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Coffee’s anti-inflammatory properties and antioxidants contribute to improved liver health.
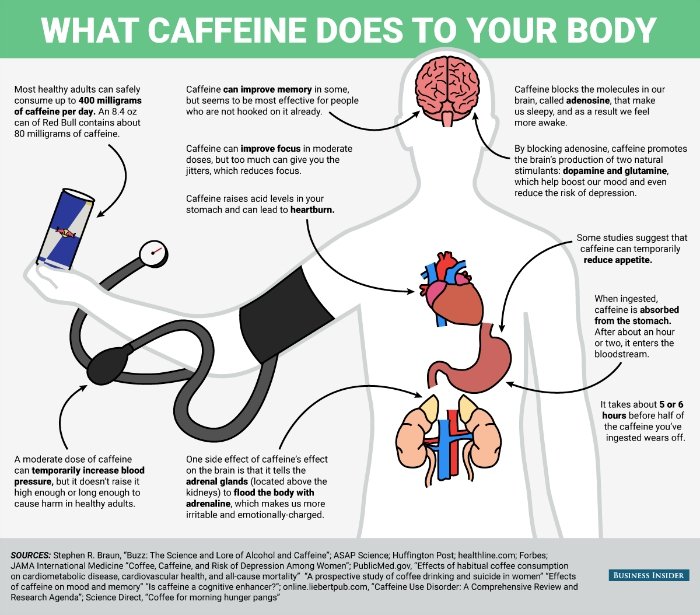
Coffee and Metabolism
Your metabolic rate determines how efficiently your body converts food into energy, and coffee can play a role in speeding up this process.
Aids in Weight Management
Caffeine increases your metabolic rate, helping you burn more calories. This can be beneficial for weight management when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Impact on Blood Sugar
Coffee’s components, such as chlorogenic acid, can influence blood sugar levels. Regular coffee consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes.
Nutritional Content of Coffee
Coffee itself is almost calorie-free and contains essential nutrients and minerals that can contribute to your daily intake.
Vitamins and Minerals
A single cup of coffee contains:
| Nutrient | Amount per 8 oz (240 ml) serving |
|---|---|
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.2 mg (11% of DV) |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) | 0.6 mg (6% of DV) |
| Manganese | 0.1 mg (3% of DV) |
| Potassium | 116 mg (3% of DV) |
| Magnesium | 7 mg (2% of DV) |
These micronutrients support various bodily functions, from energy production to maintaining healthy skin.
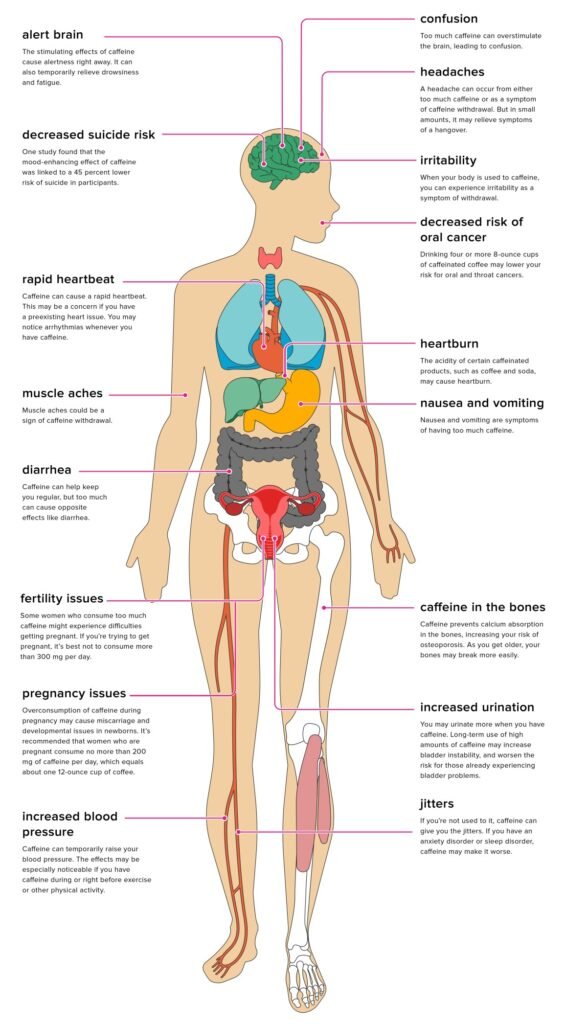
Potential Negative Effects of Coffee
While there are numerous benefits, it’s also important to consider the adverse effects that can arise from excessive coffee consumption.
Anxiety and Jitters
High caffeine intake can lead to heightened anxiety and nervousness, particularly in those with a predisposition to these conditions.
Dependency and Withdrawal
Regular consumption can lead to dependence. Sudden cessation might trigger withdrawal symptoms like headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
Digestive Issues
Overconsumption can lead to digestive troubles, such as acid reflux and heartburn. Individuals with existing gastrointestinal conditions should consume coffee cautiously.
Special Considerations for Different Population Groups
Not everyone responds to coffee in the same way. Various population groups need to consider specific factors when it comes to coffee consumption.
Pregnant Women
High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been linked to increased risks of miscarriage and low birth weight. It’s generally recommended that pregnant women limit their caffeine intake to 200 mg per day, approximately one 12-ounce cup of coffee.
Adolescents and Children
The American Academy of Pediatrics discourages coffee consumption in children and adolescents due to its potential impact on developing brains and hearts.
Older Adults
While coffee offers cognitive benefits that might be helpful for aging individuals, older adults should also be mindful of its potential to exacerbate osteoporosis or interfere with medications.

How to Maximize Coffee’s Benefits and Minimize Its Drawbacks
Approaching your coffee consumption mindfully can help you enjoy its benefits while reducing potential drawbacks.
Choose Quality Over Quantity
Opt for high-quality beans and avoid overly processed forms of coffee. Organic coffee can reduce your exposure to harmful pesticides and chemicals.
Moderation is Key
Aim to consume coffee in moderation. The general consensus for moderate coffee consumption is about 3-4 cups per day.
Timing Matters
Strategically timing your coffee consumption can maximize its benefits. Morning tends to be the best time for most people, allowing the effects to wear off by bedtime. Also, consider matching your consumption to your body’s natural cortisol production cycles, which vary throughout the day.
Be Mindful of Additives
Adding sugar, cream, and flavored syrups can turn a healthy beverage into a calorie-laden treat. Try to minimize these additives to fully reap coffee’s health benefits.
Consider Your Body’s Responses
Listen to your body. If you experience adverse effects, it might be worth reducing your intake or switching to decaffeinated options.
Conclusion
Coffee can be a wonderful addition to your daily routine, offering numerous benefits for your brain, heart, metabolism, and beyond. However, it’s essential to approach it mindfully and be aware of its potential downsides. By understanding the impact of coffee on your health and body, you can make informed choices that align with your unique needs and lifestyle. So, enjoy your cup of coffee, but do so with an awareness of how it interacts with your health and well-being.

