Is 200 mg of caffeine a lot? This is a question many people ponder as they sip their morning coffee or reach for an energy drink during a mid-afternoon slump. Understanding caffeine content and its effects on your body is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
What is Caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant most commonly found in tea, coffee, and cacao plants. It works by stimulating the brain and central nervous system, helping you stay alert and stave off the onset of tiredness. But how much is too much?
The Science Behind Caffeine
Caffeine functions by blocking the effects of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that relaxes the brain and makes you feel tired. Additionally, caffeine increases adrenaline levels and the activity of dopamine and norepinephrine in your brain. This combination keeps you awake and alert.
Daily Recommended Caffeine Intake
When it comes to safe caffeine consumption, various health organizations have differing recommendations. Let’s break it down:
| Group | Recommended Daily Limit |
|---|---|
| Healthy adults | 400 mg |
| Pregnant women | 200 mg |
| Adolescents | 100 mg |
Healthy Adults
For the average healthy adult, consuming up to 400 mg of caffeine per day is generally considered safe. This is roughly equivalent to four 8-ounce cups of brewed coffee or ten 12-ounce cans of cola.
Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should be cautious with their caffeine intake. Health experts recommend no more than 200 mg daily to reduce the risk of potential complications, such as miscarriage or preterm birth.
Adolescents
Adolescents should also be mindful of their caffeine consumption. Experts suggest a limit of 100 mg per day, as young bodies can be more sensitive to the stimulant’s effects.

Understanding 200 mg of Caffeine
To answer whether 200 mg of caffeine is a lot, it’s helpful to understand how this amount compares to common caffeinated beverages and products.
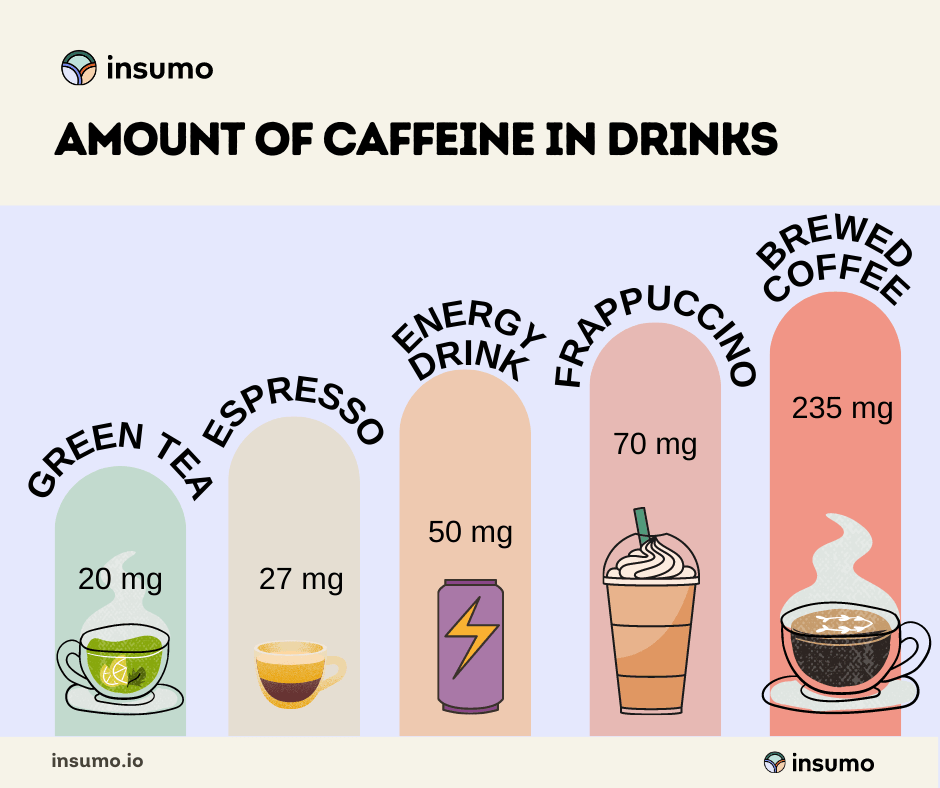
| Beverage/Product | Approximate Caffeine Content |
|---|---|
| 8 oz brewed coffee | 95 mg |
| 12 oz caffeinated soda | 30-40 mg |
| 8 oz energy drink | 70-100 mg |
| 1 oz espresso shot | 63 mg |
| 1 cup green tea | 30-50 mg |
Brewed Coffee
A standard 8-ounce cup of brewed coffee contains about 95 mg of caffeine. Therefore, consuming two such cups would total approximately 190 mg, close to the 200 mg mark.
Energy Drinks
Energy drinks often have higher caffeine content, with some containing up to 100 mg per 8-ounce serving. Drinking two cans may push you over the 200 mg limit.
Green Tea
Green tea is a milder option with 30-50 mg of caffeine per cup. To reach 200 mg, you would need to consume around four to five cups.
Effects of 200 mg of Caffeine
Understanding the impact 200 mg of caffeine has on your body can help you decide if it’s a lot for you personally.
Immediate Effects
The immediate effects of consuming 200 mg of caffeine might include increased alertness, improved focus, and a temporary energy boost. These effects are generally felt within 30 to 60 minutes of consumption.
Physical Sensations
You may also experience physical sensations, such as a faster heart rate, slight jitteriness, or even an upset stomach. These reactions can vary based on individual tolerance and sensitivity to caffeine.
Long-Term Impact
Long-term, regular consumption of moderate amounts of caffeine (such as 200 mg daily) is generally considered safe for most people. However, excessive consumption over 400 mg daily can lead to dependency, diminished sleep quality, and other health issues.
Insomnia and Sleep Disruption
Consuming 200 mg of caffeine too late in the day can disrupt your sleep. Caffeine has a half-life of about 5 to 6 hours, meaning it takes this long for half of the caffeine to leave your system. So, if you consume caffeine late in the afternoon, it might still affect your sleep.
Anxiety and Jitters
For some individuals, 200 mg of caffeine can contribute to anxiety and jitteriness, particularly if they’re sensitive to stimulants. If you find yourself feeling anxious or overly nervous, it might be worth reducing your intake.

Who Should Be Cautious with 200 mg of Caffeine?
While many people can safely consume 200 mg of caffeine, some should be more cautious.
Pregnant Women
As noted earlier, pregnant women should limit their caffeine intake to 200 mg or less per day to avoid potential pregnancy complications.
People with Heart Conditions
Individuals with certain heart conditions, like arrhythmias, should be cautious with caffeine, as it can exacerbate symptoms.
Caffeine-Sensitive Individuals
Some people are naturally more sensitive to caffeine. If you fall into this category, you may experience stronger effects even with small amounts, and 200 mg might feel excessive.
Measuring Your Caffeine Intake
Accurately measuring your caffeine intake is essential for understanding how much you’re consuming daily.
Reading Labels
Many packaged beverages and supplements display caffeine content on their labels. Make it a habit to read these labels to track your consumption.
Using Online Caffeine Calculators
Online caffeine calculators can be helpful tools. These calculators allow you to input your daily beverages and foods to estimate your total caffeine intake.

Alternatives to Caffeine
If you’re looking to reduce your caffeine intake or replace it entirely, several alternatives can help you stay energized without the stimulant effects.
Herbal Teas
Herbal teas, such as chamomile, peppermint, and rooibos, are caffeine-free and can be a soothing alternative to caffeinated beverages.
Decaffeinated Options
Decaf versions of coffee and tea provide the flavor you love without the caffeine content. Just be aware that decaf products still contain small amounts of caffeine.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining energy levels. Drinking water throughout the day can help you feel more awake and alert.
Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity can also boost your energy levels and reduce the need for caffeine. Activities like walking, stretching, or short bursts of exercise can be very effective.
Conclusion
So, is 200 mg of caffeine a lot? It really depends on your individual tolerance, lifestyle, and health considerations. For some, 200 mg may be a moderate and manageable amount, while for others, it could be excessive. Understanding your own body’s response to caffeine and monitoring your intake can help you make informed decisions about your consumption.
Remember, moderation is key. If you’re ever in doubt, consult with a healthcare provider to ensure that your caffeine habits are healthy and safe for you. This way, you can continue to enjoy your favorite caffeinated beverages without any worry.