Have you ever wondered if your daily cup of coffee could be impacting your fertility? Indeed, the relationship between coffee consumption and male fertility is a topic that has intrigued many researchers and health enthusiasts alike. Coffee is one of the most popular beverages worldwide, and it contains various compounds, the most notable of which is caffeine. But how does caffeine and coffee, in general, influence male fertility? Let’s break down this intricate topic to provide you with clear, comprehensive insights.

Understanding Male Fertility
Sperm Health and Production
Male fertility primarily depends on the health and functionality of sperm. Sperm health can be evaluated through several factors:
- Sperm Count: The concentration of sperm cells in semen.
- Sperm Motility: The movement capability of sperm.
- Sperm Morphology: The shape and structure of sperm.
Additionally, the production of sperm is influenced by factors like hormones, overall health, and lifestyle choices. Sperm health is typically assessed through a semen analysis, which measures various parameters like count, morphology, and motility.
Hormonal Balance
For optimal sperm production, maintaining a hormonal balance is crucial. Key hormones involved in this process include:
- Testosterone: The primary male sex hormone responsible for sperm production.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): Stimulates sperm production.
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH): Promotes testosterone production.
Disruptions in these hormones can lead to suboptimal sperm production and fertility issues.
Components of Coffee
Caffeine
Caffeine is the most well-known component of coffee, and it acts as a stimulant. Caffeine’s primary mode of action is blocking adenosine receptors in the brain, leading to increased alertness.
Antioxidants
Coffee is rich in antioxidants, such as polyphenols. These compounds help combat oxidative stress, which can damage cells, including sperm cells.
Other Compounds
In addition to caffeine and antioxidants, coffee contains various other bioactive compounds, like diterpenes (cafestol and kahweol), which can influence health in different ways.
Research on Coffee and Male Fertility
Caffeine Consumption and Sperm Quality
Several studies have explored the connection between caffeine intake and sperm quality. The results, however, are mixed:
Study Findings on Caffeine and Sperm Quality
| Study | Findings | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | High caffeine intake associated with reduced sperm count and motility | Potential negative impact on sperm |
| Study 2 | Moderate caffeine intake showed no significant effect on sperm parameters | No clear impact at moderate levels |
| Study 3 | Very high caffeine consumption linked to oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation in sperm | Negative impact at high levels |
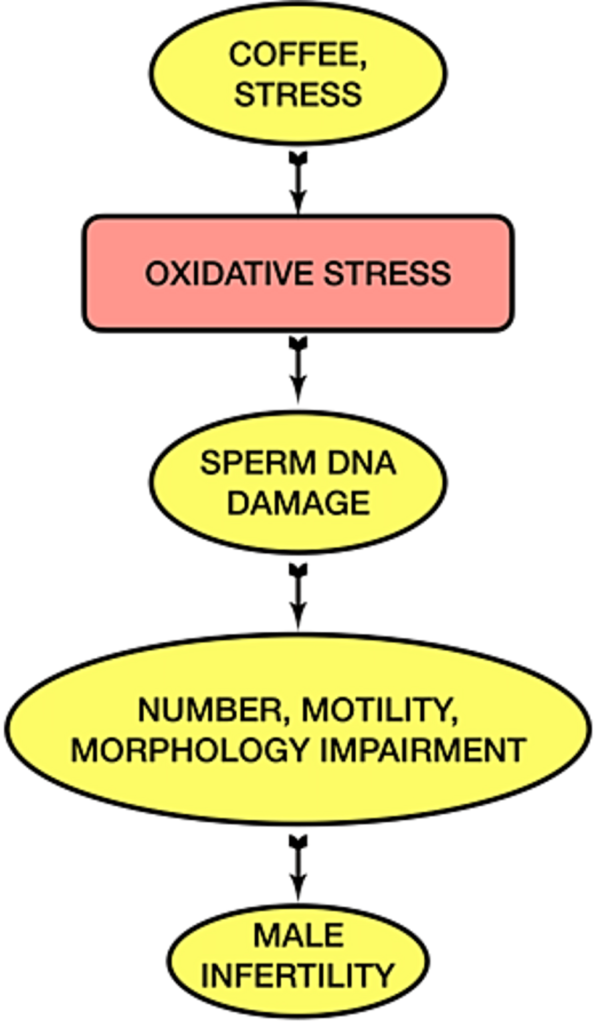
Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body. Excessive caffeine intake can elevate oxidative stress levels, potentially damaging sperm cells.
If you consume coffee in moderation, the antioxidants present could theoretically counteract some of the oxidative stress, having a neutral or even positive effect on sperm quality.
Hormonal Changes
Caffeine can impact hormone levels, including testosterone and cortisol. Studies indicate that while moderate caffeine consumption might have little to no impact, excessive intake can lead to hormonal imbalances, adversely affecting sperm production.
Lifestyle Factors and Moderation
It’s essential to consider lifestyle factors when evaluating the impact of coffee on male fertility. Factors like diet, exercise, stress levels, and other substance use (e.g., smoking and alcohol) can influence fertility more significantly than moderate coffee consumption.
How Much Coffee is Too Much?
Recommended Intake
The general guideline suggests that moderate coffee consumption—around 1-2 cups per day, providing 200-300 mg of caffeine—is likely safe for most individuals. However, exceeding this amount could lead to potential adverse effects.
Comparison to Other Sources of Caffeine
Coffee isn’t the only source of caffeine. Here’s a comparison of caffeine content in common beverages:
Caffeine Content in Beverages
| Beverage | Serving Size | Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Coffee (brewed) | 8 oz | 95 |
| Espresso | 1 oz | 64 |
| Black Tea | 8 oz | 47 |
| Green Tea | 8 oz | 28 |
| Energy Drinks | 8 oz | 80 |
| Soft Drinks | 12 oz | 39 |
Understanding caffeine content in different beverages can help you manage your overall intake more effectively.

Coffee Alternatives
Decaffeinated Coffee
Decaffeinated coffee contains significantly less caffeine, making it a potential alternative for those concerned about caffeine’s impact on fertility. Decaf coffee still offers many of the same rich flavors and some of the antioxidant benefits.
Herbal Teas
Herbal teas, such as rooibos or peppermint, are naturally caffeine-free and provide various health benefits. These can be excellent alternatives to reduce your caffeine intake without compromising on flavor.
Water and Infused Water
Staying hydrated with water or infused water (water with added fruits or herbs) is always beneficial. Proper hydration supports overall health, including reproductive health.
Practical Tips for Coffee Lovers
Monitoring Intake
Keep track of your daily caffeine consumption from all sources. This will help you ensure that you’re not unknowingly exceeding safe levels.
Balancing with Antioxidants
Incorporate antioxidant-rich foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. These can help combat oxidative stress and potentially mitigate any negative effects of caffeine on sperm quality.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management are integral to maintaining overall health and fertility. Coffee should be part of a holistic approach to your well-being.
Conclusion
So, does coffee affect male fertility? The answer isn’t entirely straightforward. Moderate coffee consumption, typically defined as 1-2 cups per day, is unlikely to significantly impact fertility for most men. However, very high caffeine intake could potentially have adverse effects on sperm quality and hormonal balance.
Given the mixed findings from studies, it’s critical to consider your overall lifestyle, dietary habits, and consumption patterns. Making informed choices and balancing your coffee intake with other healthy habits can help ensure that your caffeine enjoyment does not come at the cost of your fertility.
If you have any concerns about your fertility, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized advice and guidance based on your individual circumstances. By being mindful of your habits and maintaining a balanced lifestyle, you can continue to enjoy your favorite cup of coffee while supporting your overall health and fertility.
