What happens to your body when you quit coffee? It’s a question you might have asked yourself if you’re considering giving up that daily cup (or three) you rely on so much. Coffee is a beloved beverage around the world, often hailed for its ability to energize and invigorate. However, it also comes with its own set of cons that may have you contemplating a break from your coffee habit.
This article will guide you through the changes your body undergoes when you decide to give up coffee. Understanding these changes can make the transition smoother and help you be better prepared for what lies ahead.

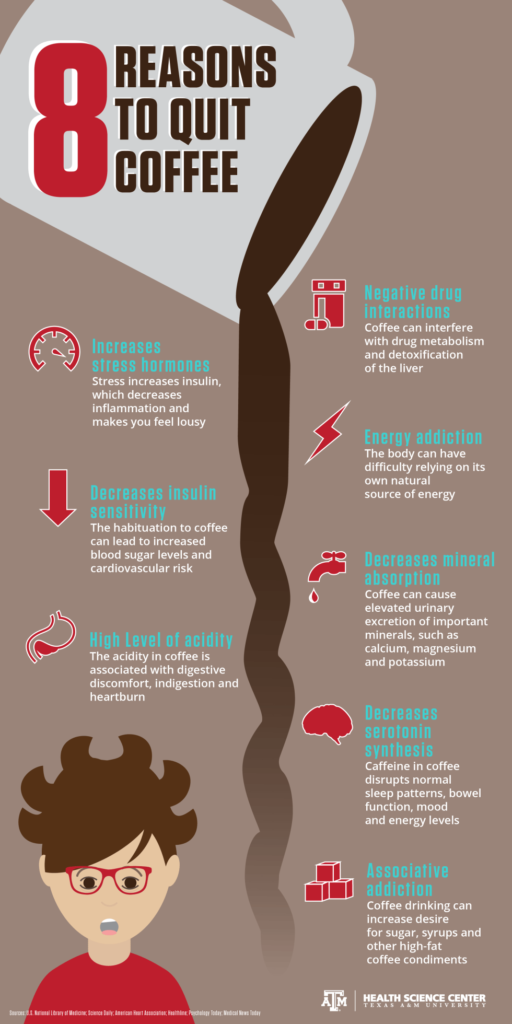
The Initial Decision: Why Quit Coffee?
Before diving into the physiological changes, it’s important to address the reasons behind your decision to quit coffee. You might find that quitting coffee helps in:
- Improving Sleep Quality: Coffee is a well-known stimulant, and even drinking it in the afternoon can interfere with your sleep cycles.
- Reducing Anxiety: Caffeine can heighten your stress levels and contribute to anxiety, which can be problematic if you’re already prone to these conditions.
- Lowering Blood Pressure: Caffeine can temporarily raise your blood pressure, putting extra strain on your cardiovascular system.
- Improving Digestion: Coffee can sometimes irritate the stomach lining and lead to digestive issues.
Psychological Aspects
Making the decision to quit coffee involves more than just physical changes; it also comes with psychological challenges. Understanding the mental component is crucial to successfully navigating this journey. You might experience cravings and a sense of missing out, especially when you see others enjoying their drinks.
The First Few Days: Immediate Changes
Withdrawal Symptoms
When you first stop drinking coffee, your body will initiate a withdrawal process. This is due to its dependence on caffeine, which has developed over time.
| Common Withdrawal Symptoms | Duration |
|---|---|
| Headaches | 2-9 days |
| Fatigue | 2-9 days |
| Irritability | 2-9 days |
| Nausea | 2-9 days |
| Muscle Pain | 2-9 days |
Energy Levels Plummet
One of the first and most noticeable changes will be a significant drop in your energy levels. Coffee acts as a stimulant, so without it, you might feel unusually tired and sluggish. This can be particularly challenging if you have a demanding work schedule or other responsibilities.
Increased Appetite
Caffeine can suppress your appetite, so you might find yourself feeling hungrier once you quit coffee. Be mindful of this change to avoid overeating or turning to unhealthy snacks.
One Week In: Settling into the New Routine
By the end of the first week, the most intense withdrawal symptoms usually start to subside. Your body begins to adapt to functioning without the regular jolt of caffeine.
Improved Sleep
One of the most significant benefits that you’ll start to notice is the improvement in your sleep quality. With caffeine out of your system, you may find it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
Enhanced Mood Stability
Without the highs and lows caused by caffeine, your mood may become more stable. You won’t experience the sharp crashes that often follow a caffeine high, making it easier to maintain a balanced emotional state.
The Second Week: Further Adaptations
Cognitive Performance
Initially, you may have felt that quitting coffee made you less sharp. However, by the second week, your cognitive functions start to adapt. Many people report that their focus and memory begin to improve, even without the aid of caffeine.
Reduced Anxiety and Stress
Caffeine can exacerbate anxiety and make you feel jittery. Without it, you may notice a significant decrease in anxiety levels. This can be a substantial benefit if you suffer from anxiety disorders or are prone to high stress.

The First Month: Long-Term Changes
Digestive Health
Quitting coffee might have some unanticipated benefits for your digestive health. Coffee can be acidic and sometimes harsh on the stomach, leading to issues like acid reflux or gastritis. Without it, your digestive system may feel more at ease, reducing instances of heartburn or stomach discomfort.
Stabilized Blood Pressure
Over time, your blood pressure may begin to stabilize. Caffeine can cause temporary spikes in blood pressure, so giving it up can have long-term cardiovascular benefits.
Natural Energy Levels
Your body will start to rely more on its own natural mechanisms to regulate energy levels. You might find that you have a more consistent supply of energy throughout the day, without the peaks and crashes associated with caffeine consumption.
The Psychological Transition: Coping Mechanisms
Finding Alternatives
One effective strategy to cope with cravings is to find suitable alternatives. Herbal teas, decaffeinated coffee, or even hot lemon water can act as substitutes. These options provide the comforting ritual of drinking a warm beverage without the caffeine.
Physical Exercise
Exercise can be a highly effective way to manage the low energy levels and mood swings that may come with quitting coffee. Activities like walking, yoga, or strength training can boost your energy and improve your mood.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Practices like mindfulness and meditation can help you manage cravings and emotional ups and downs. These techniques provide tools to stay present and focused, helping to combat the psychological challenges that come with quitting coffee.
Long-Term Benefits: Health and Well-being
Weight Management
As your appetite stabilizes and sleep improves, you may find it easier to manage your weight. Better sleep and reduced stress can contribute to a healthier lifestyle overall.
Better Hydration
Coffee is a diuretic, meaning it can cause dehydration. Without it, you’re likely to be better hydrated, which can improve overall bodily functions, including skin health and kidney function.
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
Coffee can sometimes interfere with the absorption of essential nutrients like iron and calcium. By giving it up, you may enhance your body’s ability to absorb these nutrients more effectively.
FAQs: Common Questions about Quitting Coffee
Will I Gain Weight After Quitting Coffee?
Some people may gain weight initially due to an increased appetite. However, this can be managed by making mindful food choices and incorporating regular exercise into your routine.
Can I Drink Decaf Instead?
Yes, decaffeinated coffee can be a good alternative if you miss the ritual of drinking coffee. Just be aware that decaf still contains a small amount of caffeine, which may affect some people.
How Long Will I Feel Withdrawal Symptoms?
Most people experience withdrawal symptoms that last between 2-9 days. The severity and duration can vary based on individual factors such as the amount of coffee previously consumed and your overall health.

Conclusion
Deciding to quit coffee is a significant decision that comes with its own set of challenges and rewards. From immediate withdrawal symptoms to long-term health benefits, your body undergoes a complex transformation. Understanding these changes can help you navigate this journey more smoothly. Remember, the benefits, such as improved sleep, stabilized mood, and better overall health, often outweigh the initial discomfort. By finding suitable alternatives and incorporating healthy habits, you can successfully make the switch and enjoy a caffeine-free lifestyle.
