Have you ever wondered about the amazing complexity behind the things we take for granted in our daily lives? From the tiniest cells in our body to the vastness of the universe, there’s so much to uncover, each aspect more fascinating than the last. Let’s take a journey to explore what makes our world tick, and discover the intricacies of various subjects that can enrich your understanding and appreciation of the marvelous place we call home.
What is the Universe?
The universe is everything that exists—spanning galaxies, stars, planets, and all forms of matter and energy. It is the totality of space and time, and all the physical laws and constants that govern them. The universe’s origins trace back to the Big Bang, an event that occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago, initiating the expansion of space and creating the conditions necessary for the formation of galaxies and other cosmic structures.
The Big Bang Theory
This pivotal theory posits that the universe began as a singularity, an infinitely dense point, which expanded rapidly. Since its inception, the universe has been continuously expanding, spreading galaxies farther apart. This expansion is guided by Hubble’s Law, which states that galaxies move away from us at speeds proportional to their distance.
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Singularity | A point of infinite density and temperature where the universe began. |
| Hubble’s Law | Galaxies are moving away from each other at speeds proportional to their distance. |
| Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) | Radiation leftover from the early stages of the universe, providing strong evidence for the Big Bang. |
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
A significant portion of the universe’s mass-energy content is still a mystery. Dark matter and dark energy, although invisible and undetectable by conventional means, play crucial roles in the universe’s structure and expansion. Dark matter exerts gravitational forces, holding galaxies together, while dark energy drives the universe’s accelerated expansion.
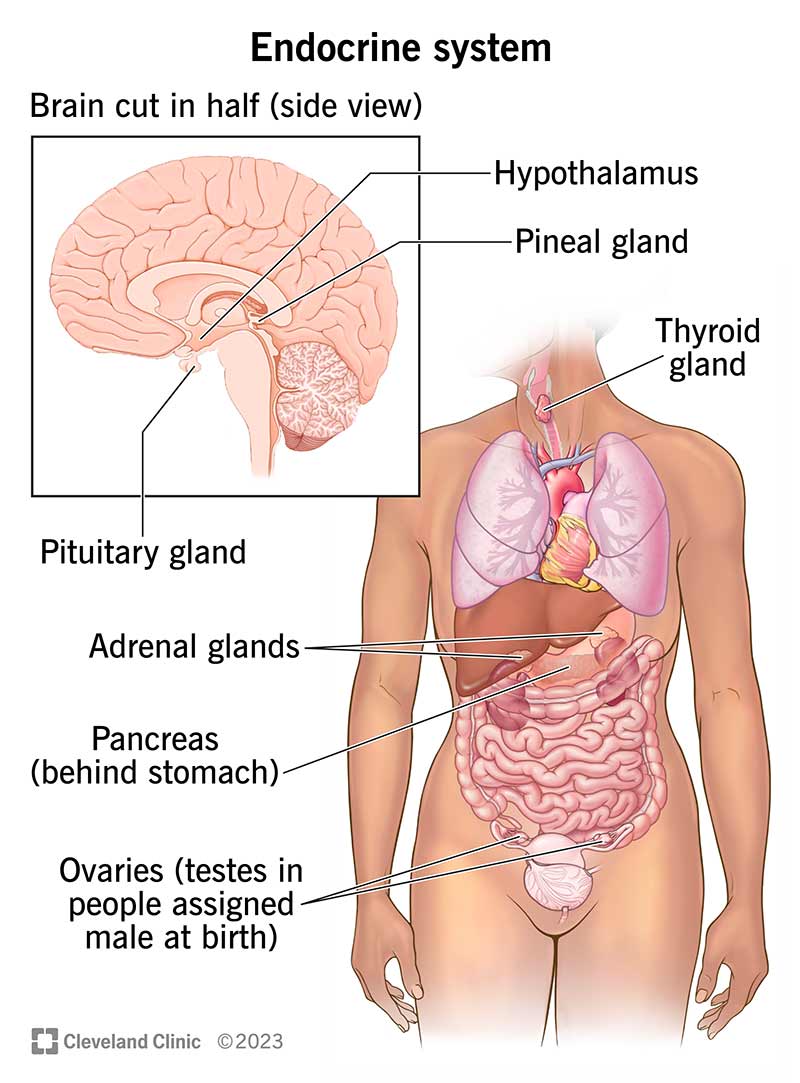
What is the Human Body?
The human body is an intricate machine composed of numerous systems working in unison. It has trillions of cells, each with specific functions, forming tissues and organs that enable complex behaviors and processes. Below, let’s break down its major components.
Skeletal System
Your skeletal system consists of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. It provides structural support, facilitates movement, and protects internal organs.
Muscular System
This system includes muscle tissues that enable voluntary and involuntary movements. Muscles work by contracting and relaxing, often in response to signals from the nervous system.
| System | Function |
|---|---|
| Skeletal System | Provides structure, protects organs, and facilitates movement. |
| Muscular System | Enables movement through muscle contractions. |
Nervous System
Your nervous system is the body’s communication network, comprising the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. It processes sensory information and coordinates responses.
Circulatory System
Consisting of the heart, blood, and blood vessels, the circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste products throughout the body. The heart pumps blood through a network of arteries, veins, and capillaries.
| System | Function |
|---|---|
| Nervous System | Processes sensory information and coordinates responses. |
| Circulatory System | Transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste products. |
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines. AI systems are designed to perform tasks that typically require human cognitive functions, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Machine Learning
A key subset of AI, machine learning involves the development of algorithms that allow systems to improve their performance based on data. Through training on large datasets, these algorithms identify patterns and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming for each specific task.
Neural Networks
Inspired by the human brain, neural networks are computing systems composed of interconnected nodes (neurons). These networks are capable of learning from data and are fundamental in deep learning, enabling advanced applications like image and speech recognition.
| AI Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Algorithms that improve through experience and data. |
| Neural Networks | Computing systems modeled after the human brain. |
Applications of AI
AI has a broad range of applications across various industries, from healthcare, where it’s used for diagnosing diseases, to finance, where it optimizes trading strategies. It also powers virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, self-driving cars, and recommendation systems used by services like Netflix and Amazon.
What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing represents a paradigm shift from classical computing, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to process information in fundamentally new ways. Unlike classical computers that use bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to a property known as superposition.
Superposition and Entanglement
Qubits can be in a state of 0, 1, or both at the same time (superposition), allowing quantum computers to perform many calculations simultaneously. Entanglement, another quantum phenomenon, links qubits such that the state of one qubit is dependent on the state of another, no matter the distance between them.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Superposition | Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously. |
| Entanglement | Qubits are interconnected, with the state of one affecting another. |
Potential and Challenges
Quantum computing holds the potential to solve complex problems that are currently intractable for classical computers, such as factoring large numbers or simulating molecular structures. However, it also faces significant challenges, including maintaining qubit stability (coherence) and mitigating errors due to decoherence.
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to long-term shifts and alterations in temperature and weather patterns. While some changes are a natural part of Earth’s climate cycle, the term commonly now refers to the accelerated change caused by human activities, particularly since the industrial revolution.
Greenhouse Gases
The primary driver of current climate change is the increase in greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to global warming and altering weather patterns.
Impacts of Climate Change
The effects of climate change are far-reaching and varied. They include more frequent and severe weather events (like hurricanes and droughts), rising sea levels due to melting ice caps and glaciers, and disruptions to ecosystems and agriculture.
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Extreme Weather Events | Increased frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, etc. |
| Rising Sea Levels | Melting ice caps contributing to higher sea levels. |
| Ecosystem Disruption | Altered habitats affecting biodiversity and agriculture. |
Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing climate change involves both mitigation and adaptation strategies. Mitigation efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy adoption, energy efficiency, and sustainable practices. Adaptation involves adjusting our lifestyles and infrastructure to the expected changes, such as building flood defenses and developing drought-resistant crops.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but its potential applications extend far beyond digital currencies. At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring that the data is immutable and transparent.
How Blockchain Works
When a transaction is made, it is grouped with other transactions into a block. This block is then added to a chain of previous blocks, forming a blockchain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring data integrity.
Consensus Mechanisms
Ensuring that all participants in a blockchain network agree on the ledger’s state requires consensus mechanisms. The most common are Proof of Work (PoW), used by Bitcoin, and Proof of Stake (PoS), which Ethereum is transitioning to. These mechanisms validate transactions and prevent double-spending.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralized Ledger | Distributed database where each participant maintains a copy. |
| Consensus Mechanisms | Methods to achieve agreement on the ledger’s state. |
Applications Beyond Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain technology is being explored for a variety of uses beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chain management, voting systems, and secure data sharing. Its inherent transparency and security features make it suitable for any application requiring trustworthy data verification.

What is Genetic Engineering?
Genetic engineering involves the direct manipulation of an organism’s DNA to alter its characteristics. This field has significant implications in medicine, agriculture, and biology, allowing scientists to enhance desired traits, eliminate diseases, or create entirely new organisms.
CRISPR-Cas9 Technology
One of the most revolutionary tools in genetic engineering is CRISPR-Cas9, a technique that allows for precise, targeted changes to the DNA sequence. It works by using a protein (Cas9) guided by a specific RNA sequence to cut the DNA at a desired location, where alterations can then be made.
Applications in Medicine
Genetic engineering holds promise for treating genetic disorders, developing targeted therapies for diseases like cancer, and creating personalized medicine based on an individual’s DNA. For example, gene therapy involves inserting, altering, or removing genes within a patient’s cells to treat genetic diseases.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| CRISPR-Cas9 | A precise tool for editing DNA at specific locations. |
| Gene Therapy | Treating diseases by modifying a patient’s genes. |
Agricultural Biotechnology
In agriculture, genetic engineering is used to develop crops with enhanced nutritional profiles, resistance to pests and diseases, and improved tolerance to environmental stresses such as drought or salinity. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are already widely used in the cultivation of crops like soybeans, corn, and cotton.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects (things) embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. This interconnected ecosystem encompasses everything from smart home devices to industrial machinery.
How IoT Works
IoT devices collect data from their environment using sensors. This data is then transmitted through communication networks to databases or other devices for analysis and action. For instance, a smart thermostat can gather temperature data and adjust heating or cooling systems automatically based on user preferences or external conditions.
Applications of IoT
The applications of IoT are vast and varied, making life more convenient, efficient, and even safer. In healthcare, IoT devices can monitor patient health and collect data for remote diagnosis. In agriculture, IoT can optimize farming practices through smart irrigation and livestock monitoring.
| Sector | Application |
|---|---|
| Smart Homes | Devices like smart thermostats, lighting, and security systems. |
| Healthcare | Remote patient monitoring, fitness trackers. |
| Agriculture | Smart irrigation, soil health monitoring. |
Challenges and Security
While IoT offers numerous benefits, it also poses challenges, particularly in terms of security and privacy. With so many connected devices, each potentially vulnerable to cyber attacks, ensuring robust security measures and data protection is crucial.
What is Renewable Energy?
Renewable energy is derived from natural resources that are replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Transitioning to renewable energy is essential for sustainable development and combating climate change.
Types of Renewable Energy
Several types of renewable energy sources are currently being harnessed:
| Type | Source of Energy |
|---|---|
| Solar Energy | Energy from the sun, captured using solar panels. |
| Wind Energy | Energy generated from wind using turbines. |
| Hydroelectric Power | Energy produced from the flow of water, typically in dams. |
| Geothermal Energy | Energy from heat stored beneath the Earth’s surface. |
| Biomass Energy | Energy from organic materials like plant and animal waste. |
Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources offer a plethora of benefits. They produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, reducing air pollution and mitigating climate change. Moreover, they are sustainable, provide energy security, and can potentially create numerous jobs in the clean energy sector.
Challenges of Renewable Energy
Transitioning to renewable energy also presents challenges. These include the intermittent nature of some sources like solar and wind, the need for substantial initial investments, and the requirement for advancements in energy storage technologies to ensure a consistent energy supply.
What is Sustainable Living?
Sustainable living involves making lifestyle choices that reduce one’s environmental impact and promote the well-being of the planet and future generations. It encompasses various practices and behaviors that contribute to environmental sustainability.
Principles of Sustainable Living
Sustainable living is guided by several core principles:
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Reducing Consumption | Minimizing waste and using resources efficiently. |
| Reusing and Recycling | Extending the life of products and repurposing materials. |
| Supporting Eco-Friendly Products | Choosing products with a lower environmental impact. |
| Energy Conservation | Reducing energy use through efficient practices and technologies. |
Everyday Practices
There are numerous ways to incorporate sustainable living into your daily routine. Simple acts like conserving water, reducing plastic usage, supporting local and sustainable products, and incorporating renewable energy sources at home can have a significant impact.
Benefits of Sustainable Living
Embracing sustainable living not only benefits the environment but also improves personal well-being. It often leads to healthier lifestyles, cost savings, and a deeper connection with nature. Additionally, it contributes to the broader goal of protecting natural resources for future generations.
Conclusion
From the wonders of the universe to the complexities of the human body, from the potentials of artificial intelligence to the promise of sustainable living, our world is a rich tapestry of interconnected phenomena and innovations. Understanding these various facets not only enhances your appreciation of the world but also equips you with knowledge to make informed decisions in your personal and professional life. By staying curious and informed, you contribute to a more knowledgeable, sustainable, and compassionate world.