Have you ever wondered if coffee might not be the ideal beverage for everyone? You’re not alone. While coffee is a beloved morning ritual for many, it’s essential to recognize that it may not be suitable for everyone due to various health considerations. In this article titled “Who Should Not Drink Coffee: Important Health Considerations,” you will find detailed information on who should be cautious about drinking coffee and why.
Caffeine Sensitivity and Intolerance
Understanding Caffeine Sensitivity
Caffeine sensitivity varies significantly among individuals. Some people can enjoy multiple cups of coffee without any issues, while others may experience adverse reactions even after a small amount. This sensitivity largely depends on your genetic makeup and how your body metabolizes caffeine. If you find yourself feeling jittery, anxious, or having trouble sleeping after consuming coffee, you may have a higher sensitivity to caffeine.
Symptoms of Caffeine Intolerance
Caffeine intolerance is a more severe form of sensitivity. Symptoms can include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach upset, acid reflux, or diarrhea. In some cases, individuals may experience rapid heartbeat, dizziness, or extreme fatigue after the effects of the caffeine wear off. If you notice these symptoms after consuming coffee, it might be best to limit or avoid it altogether.
Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Risks During Pregnancy
Pregnant women need to be particularly cautious with their caffeine intake, as high levels of caffeine can lead to adverse pregnancy outcomes, including miscarriage and preterm birth. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends limiting caffeine consumption to less than 200 milligrams per day, which is roughly equivalent to one 12-ounce cup of coffee.
Impact on Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding women should also be mindful of their caffeine consumption. Caffeine can pass into breast milk and potentially affect your baby, leading to irritability and disrupted sleep patterns. It’s advisable to monitor your caffeine intake and observe your baby’s reactions.
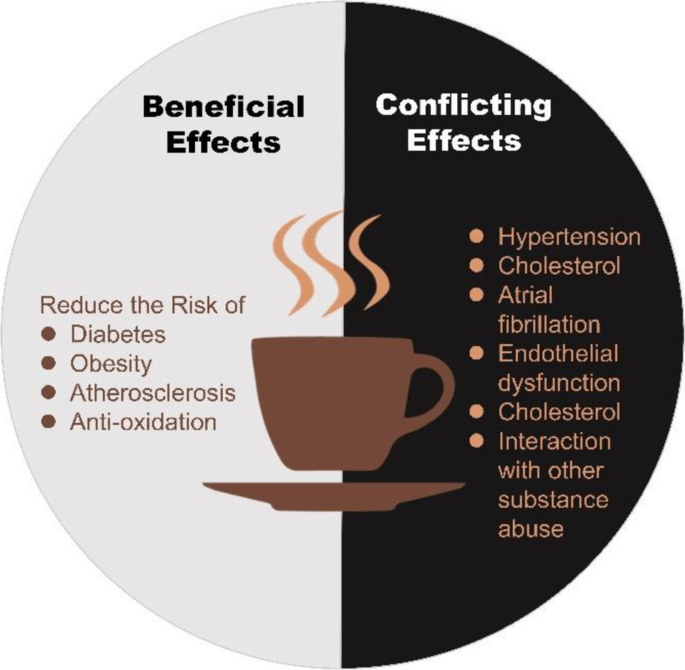
People with Heart Conditions
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Individuals with hypertension should be cautious about coffee consumption. Caffeine can cause a temporary spike in blood pressure, which might be dangerous for those with high blood pressure. Research suggests that habitual coffee drinkers might not experience as significant a blood pressure increase as occasional drinkers, but it’s still wise to consult your healthcare provider to determine a safe level of consumption.
Heart Arrhythmias
Heart arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats can also be exacerbated by caffeine. Those with conditions such as atrial fibrillation (AFib) might notice their symptoms worsening with caffeine intake. If you have a history of heart arrhythmias, moderating or avoiding coffee might be beneficial.
Individuals with Gastrointestinal Issues
Acid Reflux and GERD
Coffee is known to trigger acid reflux and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) in some individuals. The high acidity and caffeine content can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acids to flow back into the esophagus, causing discomfort and heartburn. If you suffer from these conditions, reducing or eliminating coffee might help alleviate symptoms.
IBS and Other Digestive Disorders
People with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or other digestive disorders may find that coffee irritates their digestive tract, leading to cramps, diarrhea, or indigestion. If you have a sensitive digestive system, you might want to consider switching to low-acid coffee or other beverages.

Anxiety and Sleep Disorders
Anxiety Disorders
Caffeine is a stimulant that can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety disorders. If you suffer from generalized anxiety disorder, panic attacks, or social anxiety, coffee might increase your feelings of nervousness or trigger anxiety episodes. It’s essential to monitor how caffeine affects your anxiety levels and adjust your intake accordingly.
Insomnia and Other Sleep Disorders
Caffeine can significantly impact your sleep quality and duration. If you have insomnia or other sleep disorders, consuming coffee, especially in the afternoon or evening, can make falling and staying asleep more difficult. Limiting your caffeine intake earlier in the day or switching to decaffeinated options might improve your sleep patterns.
Children and Adolescents
Impact on Development
Children and adolescents are more sensitive to caffeine than adults. High caffeine intake can interfere with brain development, sleep patterns, and increase the risk of developing anxiety and behavioral issues. It’s generally recommended that young people limit their caffeine consumption to avoid these potential negative effects.
Behavioral Issues
Caffeine can contribute to behavioral problems in children and teens, such as hyperactivity, difficulty concentrating, and mood swings. Parents should be mindful of their children’s caffeine intake from all sources, including soda, energy drinks, and certain medications.

People Taking Certain Medications
Interaction with Medications
| Medication Type | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Can enhance stimulant effects, increasing the risk of side effects |
| Antidepressants | May interact with caffeine, affecting the drugs’ efficacy and side effects |
| Stimulants | Combined with caffeine, can lead to overstimulation and serious health risks |
| Heart Medications | Can cause increased heart rate and blood pressure |
Some medications can interact adversely with caffeine, either by enhancing its stimulant effects or by causing harmful side effects. Always consult your healthcare provider about your caffeine consumption if you’re taking medication.
Common Over-the-Counter Medications
Certain over-the-counter medications, such as cold and flu remedies, pain relievers, and diet pills, may contain caffeine. When combined with coffee, this can lead to excessive caffeine intake, resulting in side effects such as jitteriness, rapid heartbeat, or headaches. Be sure to read labels and be aware of all sources of caffeine.
Diabetics and Blood Sugar Management
Effects on Blood Sugar Levels
Coffee can affect blood sugar levels both positively and negatively. For some people, caffeine may improve insulin sensitivity, while for others, it can cause spikes in blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes, monitoring your blood sugar levels and noting any changes after consuming coffee can help you decide if it’s a suitable beverage for you.
Concerns with Additives
Many coffee drinks, especially those from popular coffee chains, contain significant amounts of sugar and other additives. These ingredients can quickly turn a seemingly harmless cup of coffee into a high-calorie, high-sugar beverage that can be detrimental to blood sugar management. Opt for plain coffee or use sugar substitutes to avoid these issues.

Individuals with Osteoporosis
Calcium Absorption
High caffeine intake can interfere with calcium absorption, which is crucial for bone health. For individuals with osteoporosis or those at risk for the condition, reducing coffee consumption can help ensure that your body absorbs enough calcium to maintain bone density.
Recommended Alternatives
If you’re concerned about bone health, consider switching to beverages that are fortified with calcium, such as certain plant milks. You can also look for decaffeinated coffee options, which have significantly lower caffeine levels.
Adolescents and Teenagers
Developmental Concerns
Adolescents and teenagers are still growing, and excessive caffeine intake can interfere with their development. High caffeine consumption during these formative years can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, which is crucial for growth and brain development.
Recommendation for Teenagers
It’s generally recommended that teenagers limit their caffeine intake to no more than 100 milligrams per day, which is about the amount in one cup of coffee. Parents should monitor their teens’ caffeine consumption from all sources and encourage healthier beverage choices.

Liver Health Concerns
Liver Diseases
Individuals with certain liver conditions need to be cautious with their caffeine intake. While some studies suggest that moderate coffee consumption can be beneficial for liver health, excessive intake might not be advisable for everyone. Those with liver disease should consult their healthcare provider to determine an appropriate level of coffee consumption.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Moderate coffee consumption has been associated with a lower risk of liver diseases such as cirrhosis and liver cancer. However, balance is key, and those with pre-existing liver conditions should always seek medical advice before making coffee a regular part of their diet.
Impact on Oral Health
Staining and Enamel Erosion
Coffee can cause staining of the teeth due to its dark color. Over time, coffee consumption can also lead to enamel erosion, making teeth more vulnerable to cavities and decay. Practicing good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly can help mitigate these effects.
Bad Breath
Coffee can contribute to bad breath, known as halitosis. This is because coffee can cause a reduction in saliva production, which is necessary for keeping your mouth clean. If you’re concerned about bad breath, consider rinsing your mouth with water after drinking coffee or using a mouthwash.
Psychological Dependence
Understanding Caffeine Dependence
While not officially classified as an addiction, caffeine dependence is a recognized condition. Over time, your body can become accustomed to regular caffeine intake, leading to withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, irritability, and fatigue if you suddenly stop consuming it. If you find that you can’t function without your daily coffee fix, you might be experiencing caffeine dependence.
Managing Dependence
Gradually reducing your caffeine intake can help manage dependence. You might want to switch to decaf coffee or reduce the number of cups you drink daily. Finding alternative sources of energy, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also help you rely less on caffeine.
Conclusion
It’s clear that while coffee can be a delightful and energizing beverage for many, it’s not suitable for everyone. Recognizing the potential health implications of coffee consumption based on individual circumstances and health conditions is crucial. Whether you have specific health concerns, are pregnant or breastfeeding, have a sensitive digestive system, or are managing a chronic condition, understanding how coffee affects your body can help you make more informed choices. Always consider consulting your healthcare provider to discuss your coffee consumption and ensure it aligns with your overall health and wellness objectives.
